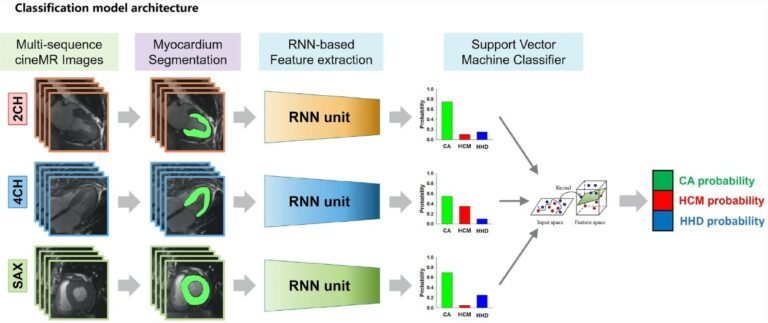
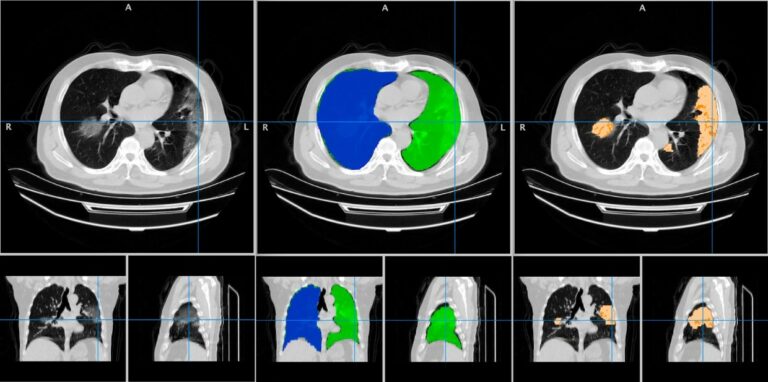
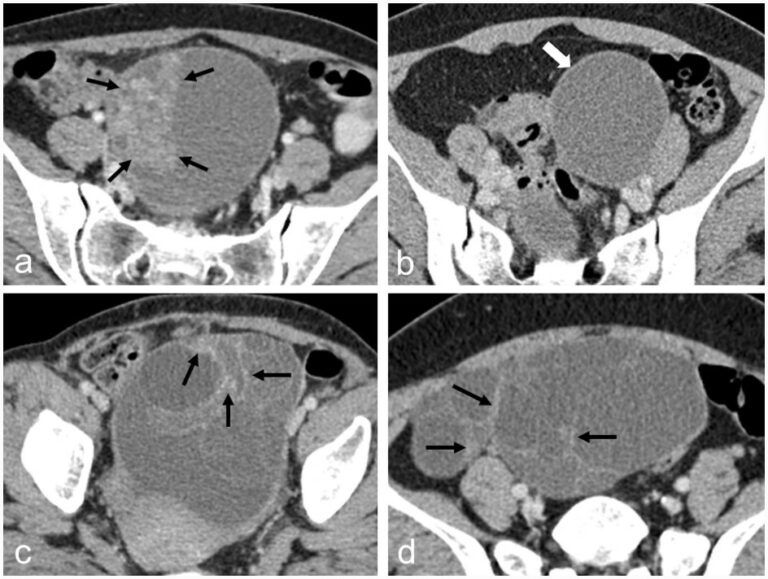
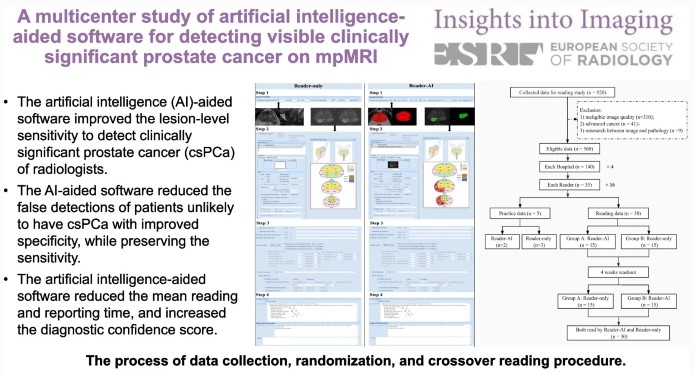
Evaluation of techniques to improve a deep learning algorithm for the automatic detection of intracranial haemorrhage on CT head imaging
This study evaluates deep learning (DL) algorithms that are playing an increasingly important role in automatic medical image analysis. The DL algorithm used was trained and externally evaluated on open-source, multi-centre retrospective data that contained radiologist-annotated non-contrast CT head studies. The authors concluded that the DL model has applications in a triage role with the potential to improve diagnostic yield